The Keto Diet is a low-carb, high-fat diet that has many similarities with the Atkins and low-carb diets. It involves drastically reducing carbohydrate ingestion and replacing it with fat. This shifts the body’s metabolism away from glucose and towards fat as its primary fuel source, which can help people to lose weight.
Keto Diet is a popular diet that has been around for decades. The term keto was first coined in 1923 when Dr. Russell Wilder described the effects of fasting on epilepsy patients in his practice at Johns Hopkins Medical Center in Baltimore, Maryland.
How It Works
When you consume fewer carbohydrates (carbs) a day, your body ultimately runs out of energy (sugar), which is used by the body to perform various activities. It forces the body to burn stored fat molecules instead of carbohydrates for energy. Ketones are produced when your liver breaks down fats for energy, which are then released into the bloodstream. Your body will begin using ketones as fuel if you don’t get enough glucose (blood sugar) from food. Your brain also relies on ketones as an alternative fuel source. Ketones are used as fuel by all cells in your body except red blood cells. Red blood cells need glucose to survive. So, when you’re not eating enough carbohydrates, your body will use ketones as fuel.
How Long Does It Take To Reach Ketosis?
Once you’ve decided to try the keto diet, you’ll likely be asked how long it takes to go into ketosis. This process varies from person to person, so there’s no exact answer. However, most experts agree that it takes three to four days before your body starts burning fat as fuel instead of carbohydrates.
Why Should I Try Keto?
The ketogenic diet may improve your mood and reduce cravings for sweets and carbs. In fact, studies have shown that people in a state of keto-adaptation have a higher cognitive function and improved memory compared to those who aren’t.
There are many other benefits of the Ketogenic diet which are listed below
- Weight Loss
The keto diet helps you lose more weight in several ways, including boosting metabolism and reducing appetite.
A ketogenic diet comprises of foods that fill a person up. This decreases the production of appetite-stimulating hormones, such as insulin and ghrelin, and increases the leptin hormone. The increased amount of Leptin and decreased amount of ghrelin and insulin decrease hunger. And when you are less hungry, you eat less. But in order to perform its many functions, your body requires energy constantly. Your body then burns body fat for energy since it has little to no access to carbs to use as fuel, which results in the production of a chemical called ketone in your liver. Your body thus enters a condition of ketosis.
The body’s primary fuel source on a diet, ketone bodies, has a direct function in lowering hunger and increasing calorie expenditure as a result of how fat and protein are metabolically converted into glucose. In this way, you reduce fats and thus weight. In a research of 13 independent randomized controlled trials, participants who followed ketogenic diets lost 2 pounds in a period of 1-3 months.
- Improves acne
Following a diet high in refined and processed carbs may alter the balance of gut bacteria and induce major swings in blood sugar, both of which can alleviate acne symptoms in some people.
- Seizures
According to the Epilepsy Foundation, ketosis can lessen seizures in patients with epilepsy, particularly those who have not responded to conventional treatment options. More study is needed to determine how beneficial this is; however, it appears to be most useful in children who experience focused seizures.
- Diabetes
Since the keto diet eliminates sugar and most carbs, it’s easy to understand why it is good for blood sugar control. The fewer sugar and carbohydrates you consume, the less sugar is present in your bloodstream. This is why, very immediately after beginning a keto diet, most people will experience a reduction in their blood sugar. In fact, the effects are so quick that diabetics who begin a ketogenic diet should collaborate with their healthcare physician to alter their medication as needed when their glucose levels drop and become more stabilized.
Furthermore, as previously said, lowering carbs depletes your body’s glucose reserves, causing your body to begin using fat for fuel rather than carbohydrates/glucose. Because your body is no longer required to manage a large amount of sugar, your insulin levels fall.
The ketogenic diet is beneficial to persons with insulin resistance as well. Insulin resistance occurs when the body stops responding properly to insulin. This frequently results in increased blood glucose levels, which can develop into diabetes and raise your risk of heart disease over time. Diabetes patients who embraced a ketogenic diet showed significant decreases in their glucose-lowering drugs and fasting glucose levels, according to studies.
- Blood Pressure
Anyone suffering from high blood pressure will embrace the excellent blood pressure management that a keto diet provides.
In trials of obese individuals, those on a ketogenic diet had a greater drop in blood pressure than those on low-fat diets. Furthermore, in the ketogenic group, systolic blood pressure was reduced (which is beneficial for controlling high blood pressure), but it rose in the low-fat/diet-drug-medication group.
- Cancer
According to preliminary research, the ketogenic diet may slow the growth of malignant tumors. When most people discuss keto as a cancer therapy, they’re referring to the Warburg effect, which states that cancer cells prefer anaerobic (without oxygen) glycolysis to make energy.
This is substantially less effective than aerobic glycolysis, implying that cancer cells require much more glucose for energy.
The most intriguing aspect is that some tumors lack the capacity to utilize ketone bodies. This indicates that if such cancer does not have access to sugar for energy, it will die. A ketogenic diet basically “starves” the cancer cells in these circumstances. Unfortunately, not all tumors behave in the same manner, and the Warburg effect is not universally observed in all cases.
- Better Sleep
The keto diet has also been proven to enhance sleep quality. Initially, falling asleep may be challenging, especially during the first week of your keto diet. However, after your body has adapted to ketosis, you will find it easier to fall asleep, sleep deeper, and wake up feeling more relaxed and refreshed.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
When a woman’s ovaries become bigger than normal, tiny fluid-filled sacs develop around the eggs. It can be caused by high levels of insulin. Ketogenic diets, which reduce both the amount of insulin you create and the amount you need, combined with other lifestyle modifications like exercise, deep sleep, and weight loss, may help cure it.
- Heart Health
A greater level of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) is linked to a reduced risk of heart problems. One of the most effective strategies to upraise your HDL levels is to consume more fat. This might explain why, on low-carb diets, HDL levels tend to increase, but on low-fat diets, they tend to drop.
- Reduce Inflammation Markers
Inflammation levels may suggest your present risk of acquiring health diseases such as arthritis, heart disease, and even immunity issues. Doctors can assess your inflammation levels by examining high-sensitivity C-reactive proteins (hsCRP) and white blood cell counts. In a two-year survey, individuals who followed a low-carb diet had a 29% reduction in their hsCRP levels.
- Brain Health
According to several pieces of research, the ketones produced during the keto diet have positive neuroprotective effects, which means they help strengthen and protect the brain and nerve cells.
- Other Nervous System Disorders
The Ketogenic diet has an impact on your spinal chord, brain, and the nerves that connect them. This diet may assist with a variety of conditions, including epilepsy, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and sleep disturbances. Scientists aren’t sure why, but it’s possible that the ketones produced by your body preserve your brain cells from injury.
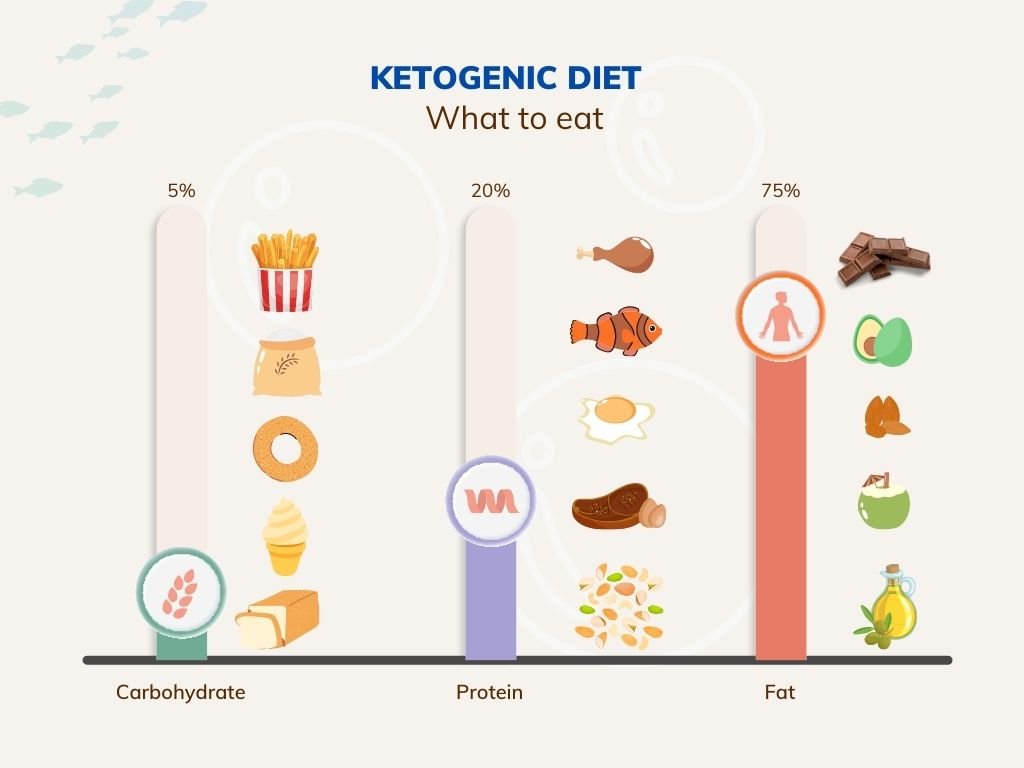
Foods to eat on a ketogenic diet
- Fish and Seafood
Fish and other seafood items are rich in B vitamins, potassium, selenium, and omega-3 fats. These types of food items not only decrease the risks of many chronic diseases but also improve brain and bodily health.
- Low carb Vegetables
Vegetables like broccoli, cauliflower, cabbage, spinach, asparagus, green beans, bell peppers, zucchini, and brussels sprouts are all keto friendly. These veggies are rich in fiber and antioxidants. These also have vitamin C and various amounts of minerals in them and can protect against cell damage.
- Mushrooms
Mushrooms contain nearly no carbohydrates but are high in other nutrients like B and D vitamins, potassium, and selenium. They have also been demonstrated to have powerful anti-inflammatory effects.
- Dairy and dairy products
Milk, Yogurt, cheese, cream, butter, and other related products are rich in calcium, protein, and fats. These can reduce appetite and prevent many heart and bone diseases.
- Meat and poultry products
These are considered as a staple food and are rich in Vitamins B, protein, and several other minerals and help in building muscles. Eggs have high amounts of antioxidants, lutein, and zeaxanthin, which protect eye health.
- Fruits
◾ Berries are an exception to the rule that most fruits are too rich in carbohydrates to eat on the keto diet. Berries, including blackberries, blueberries, raspberries, and strawberries, are high in antioxidants, which assist in alleviating inflammation and protect against illness.
◾ Avocados are strong in monounsaturated fat and potassium, a mineral deficient in many parts of the world. A half of a medium-sized avocado has 9 grams of carbs and 7 grams of fiber. Switching from animal to plant fats, such as avocados, can help lower cholesterol and triglyceride levels.
- Other foods and beverages
◾ Nuts and seeds: these help in the prevention of various heart problems, certain types of cancers, depression, and other chronic diseases
◾ Coffee and Tea: Unsweetened coffee and tea are nearly carbs and fat-free. Also, caffeine is present in coffee and tea, which stimulates metabolism and boosts physical performance, alertness, and mood.
◾ Dark Chocolates: Dark chocolate is a tasty complement to the keto diet. They not only taste nice, but they are also high in antioxidants known as flavonols, which may help decrease blood pressure and keep arteries healthy.
NOTE:
- Consult your doctor before running into the Keto diet because your doctor may prescribe you the best diet according to your body type.
- Patients with type 1 diabetes and other generic diseases are not recommended to start the Keto Diet plan.